Running is a fantastic way to stay fit, relieve stress, and enjoy the outdoors. However, like any physical activity, it carries the risk of injuries. Whether you are a seasoned runner or just starting your running journey, understanding the most common running injuries and how to prevent and treat them is essential. In this blog, we will explore some of the frequently encountered running injuries, their causes, and effective strategies for recovery.
Shin Splints:
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are characterized by pain along the shinbone (tibia). This injury is often caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the shin muscles and tendons. Common risk factors include improper footwear, running on hard surfaces, sudden increase in training intensity, or poor running form.
Prevention and Treatment:
Gradually increase training intensity and mileage.
Invest in proper running shoes with adequate cushioning and support.
Strengthen lower leg muscles through targeted exercises.
Apply ice packs to reduce pain and inflammation.
Rest and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
Plantar Fasciitis:
Plantar fasciitis is the inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. Runners often experience heel pain, especially after prolonged rest or during the first few steps in the morning. Contributing factors include tight calf muscles, high arches, improper footwear, or sudden increase in mileage or intensity.
Prevention and Treatment:
Wear supportive and well-fitting running shoes.
Incorporate stretching exercises for the calves and plantar fascia into your routine.
Gradually increase running intensity and distance.
Use orthotic inserts or arch supports if necessary.
Apply ice and massage the affected area to alleviate pain.
IT Band Syndrome:
The iliotibial (IT) band is a thick band of fascia running along the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee. IT band syndrome occurs when the IT band becomes tight or inflamed, leading to knee pain. Common causes include repetitive bending and straightening of the knee, downhill running, or muscle imbalances.
Prevention and Treatment:
Incorporate strength and flexibility exercises for the hips and thighs.
Avoid sudden increases in training intensity or mileage.
Use a foam roller to release tension in the IT band.
Cross-train with activities that reduce impact on the knees.
Consult a physical therapist for specific exercises and treatment options.
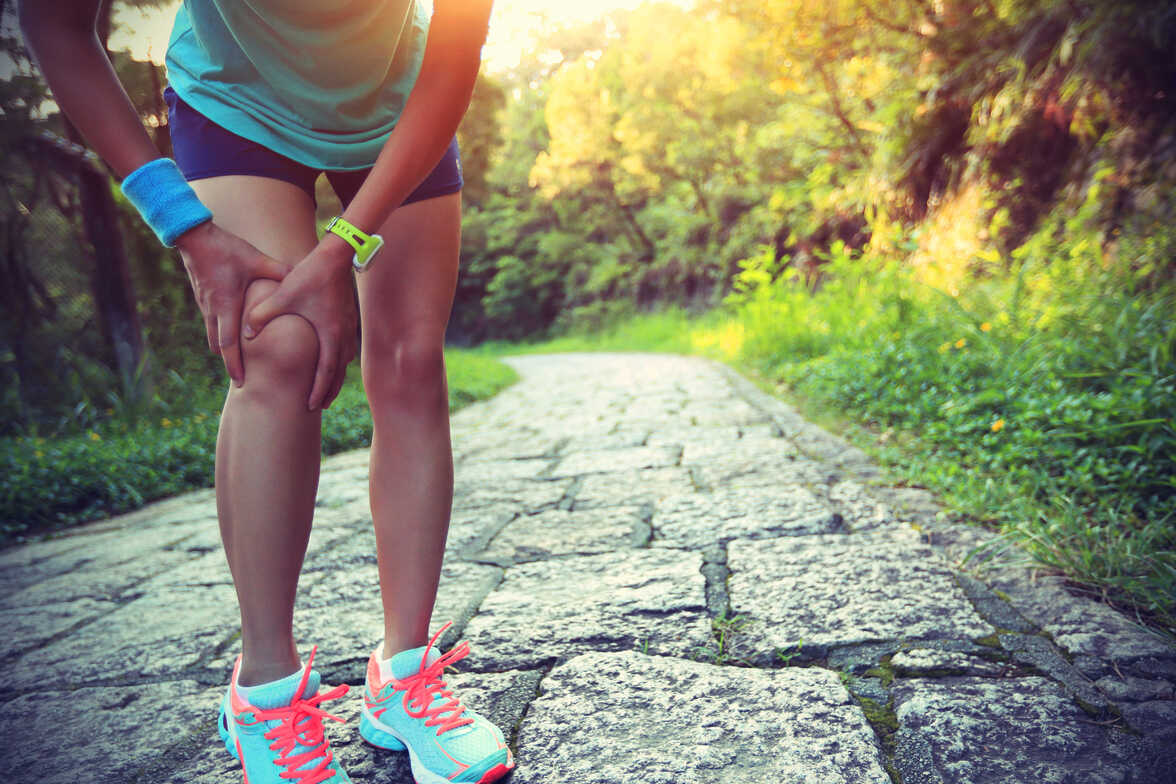
Runner's Knee (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome):
Runner's knee is a general term referring to pain around or behind the kneecap. It is often caused by improper tracking of the kneecap during running, leading to inflammation and irritation. Factors such as muscle imbalances, overpronation, or running on uneven surfaces can contribute to this condition.
Prevention and Treatment:
Strengthen the quadriceps and hip muscles to improve knee alignment.
Use proper footwear and consider orthotic inserts if needed.
Avoid excessive downhill running.
Apply ice to reduce inflammation after running.
Modify running surfaces to minimize impact on the knees.
Conclusion:
While running injuries can be frustrating, they are often preventable with the right precautions and management strategies. Remember to listen to your body, gradually increase your training, and prioritize proper form and footwear. If you experience persistent or severe pain, it is essential to seek professional medical advice. By taking care of your body and addressing running injuries promptly, you can continue to enjoy the many benefits of running for years to come. Happy and injury-free running!

Atoosa Khosh-Ghalb
Contact Me